Can Pigmentation Be Cured Permanently? is a question asked by many, but first let’s understand what pigmentation is. Pigmentation is a common skin condition that can affect individuals in various ways. Many people experience dark spots or uneven skin tones, which can be frustrating and impact self-esteem. This article aims to explore the possibilities of curing pigmentation permanently.
First, let’s understand what pigmentation is and the different types that exist. Some people may deal with hyperpigmentation, where certain areas of the skin become darker due to excess melanin. Others might face hypopigmentation, which is the loss of skin color.

We’ll also take a closer look at the causes of pigmentation, including genetic factors, environmental influences, and hormonal changes. Understanding these aspects is essential in determining the right treatment options.
Finally, we will discuss various treatments available and factors that can influence their effectiveness. By examining these elements, we can better understand if a permanent cure for pigmentation is possible.
Table of Contents
Understanding Pigmentation
Before addressing whether pigmentation can be cured, it is essential to understand what pigmentation is. This section will outline the types of pigmentation and their characteristics, helping to lay the groundwork for our discussion on treatments and potential cures.
What is Pigmentation?
Pigmentation refers to the coloring of the skin, which is primarily caused by melanin, a pigment produced by cells known as melanocytes. Melanin is responsible for the natural color of our skin, hair, and eyes. An imbalance in melanin production—whether too much or too little—can lead to various pigmentation disorders. Understanding this balance is crucial, as it influences how our skin responds to different factors, including sun exposure, hormonal changes, and skin injuries.
Types of Pigmentation
There are primarily two categories of pigmentation disorders: hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation. Each type has its own characteristics and causes.
Hyperpigmentation
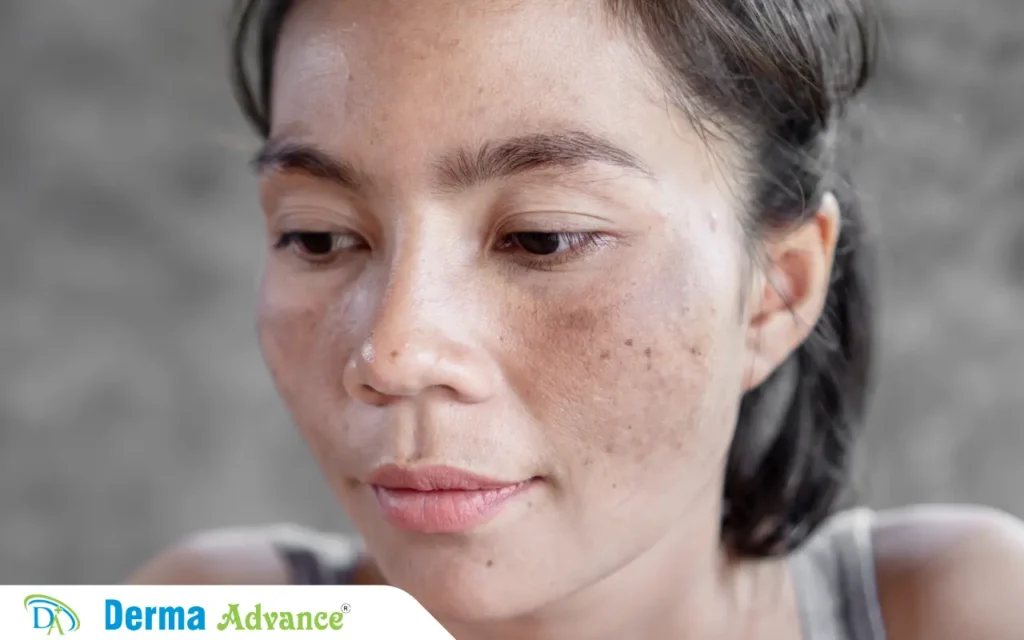

Hyperpigmentation is the condition where certain areas of the skin become darker than the surrounding skin due to an excess of melanin. This can occur in various forms, with some common types including:
Sunspots
Also known as solar lentigines, sunspots are dark patches that typically appear on areas of the skin that have been exposed to the sun for extended periods. These spots are more common in older adults and are caused by cumulative sun damage over the years. Protecting the skin with sunscreen can help prevent further darkening and the development of new spots.
To learn more about them you can read more from our page on Dark Spot Removal Tips.
Melasma
Melasma is characterized by brown patches that typically appear on the face, especially on the cheeks, forehead, and upper lip. This condition is often triggered by hormonal changes, such as those that occur during pregnancy or while taking birth control pills. It can also be exacerbated by sun exposure. Treatment may involve topical creams, laser therapy, or chemical peels to help reduce the appearance of these patches.
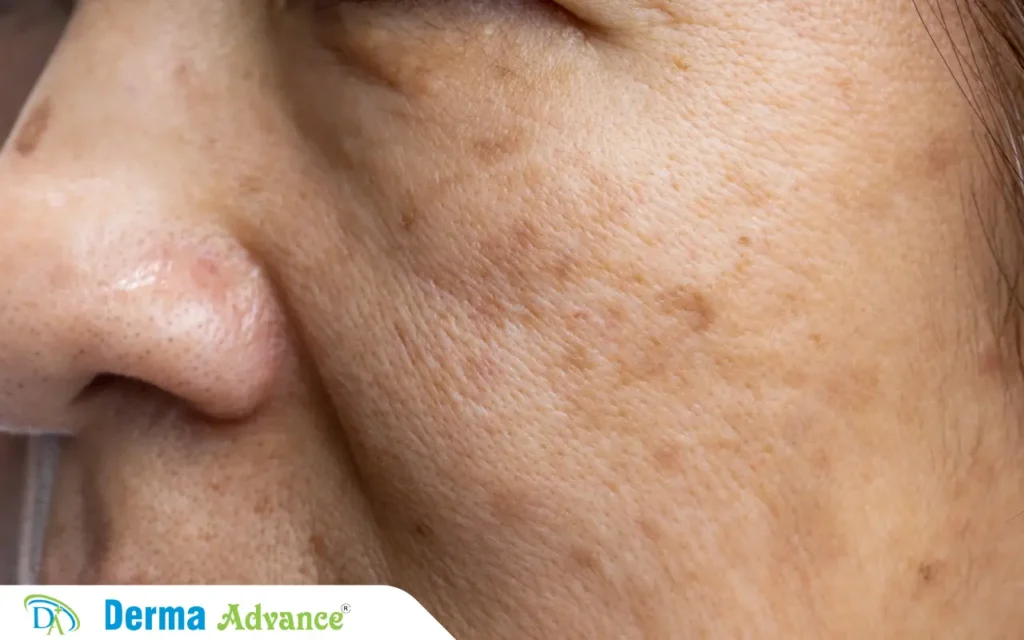
To learn more about them you can read more from our page on Melasma Treatment.
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation
This type of hyperpigmentation occurs after an injury to the skin or as a result of inflammation, such as acne scars. When the skin heals, it may leave behind darker spots where the injury occurred. This condition can be particularly frustrating for those with acne, as it can take a significant amount of time for these dark spots to fade.
Hypopigmentation
Hypopigmentation, on the other hand, refers to the loss of skin color due to a reduction in melanin. This condition can lead to lighter patches of skin and is seen in various disorders, including:
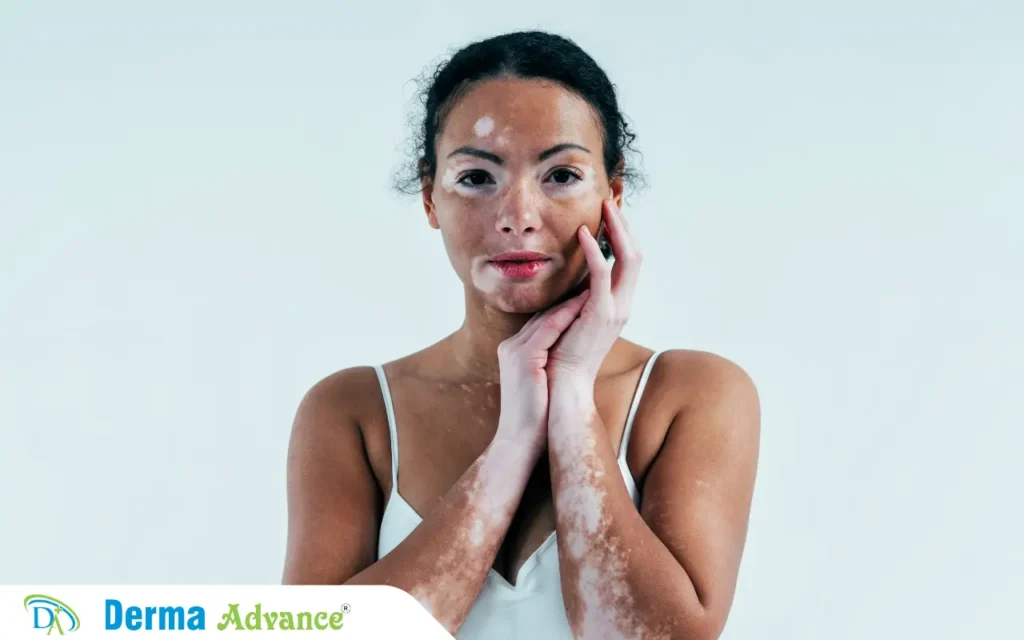

- Vitiligo: A long-term skin condition that causes patches of skin to lose their pigment.
- Albinism: A genetic condition characterized by the absence of melanin in the skin, hair, and eyes.
Understanding these types of pigmentation is crucial in determining appropriate treatments and whether permanent solutions are feasible. The journey to addressing pigmentation issues starts with identifying the specific type and its underlying causes. To learn more about albinism visit Mayo Clinic.
Causes of Pigmentation
Understanding the underlying causes of pigmentation is crucial in determining treatment options and the potential for a cure. Various factors contribute to pigmentation disorders, including genetics, environmental influences, hormonal changes, and skin injuries. Each of these causes plays a unique role in how pigmentation develops, and recognizing them can help in choosing the most effective treatments.
Genetic Factors
Genetics can significantly influence an individual’s predisposition to certain pigmentation issues. Family history may play a pivotal role in conditions like melasma or vitiligo. For instance, if a parent or sibling has melasma, the likelihood of developing it may increase due to inherited genetic traits. Studies have shown that individuals with a family history of pigmentation disorders often share similar skin types and sensitivities, which can affect melanin production.

Moreover, genetic factors can also determine how the skin reacts to environmental stimuli. For example, people with darker skin tones may experience hyperpigmentation more readily after skin trauma, while those with lighter skin may be more prone to hypopigmentation. Understanding these genetic links is essential for personalized treatment plans.
To learn more about them you can read more from our page on Role of Genetics in Acne.
Environmental Factors
Environmental influences play a significant role in the development and exacerbation of pigmentation disorders. One of the most critical factors is exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. Prolonged sun exposure can trigger the production of excess melanin, leading to conditions like sunspots and premature aging of the skin. Even on cloudy days, UV rays can penetrate the skin and contribute to pigmentation changes, making it vital to protect the skin consistently.
Pollution is another environmental factor that can affect skin pigmentation. Airborne pollutants can cause oxidative stress, leading to inflammation and pigmentation disorders. Ingredients found in skincare products can also act as irritants, leading to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) in sensitive individuals. Therefore, incorporating sun protection and antioxidants into a daily skincare regimen is crucial for preventing and treating pigmentation issues.
To learn more about them you can read more from our page on Role of Sunscreen.
Hormonal Influences
Hormonal fluctuations are particularly significant in women and can trigger various pigmentation disorders, including melasma. Melasma is often seen during pregnancy, known as the “mask of pregnancy,” and is caused by hormonal changes that increase melanin production. Hormonal therapies, such as birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy, can also exacerbate melasma in susceptible individuals.
Additionally, conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can lead to hormonal imbalances that affect skin pigmentation. Monitoring and managing hormonal levels can be an essential aspect of treatment for those experiencing pigmentation disorders related to hormonal changes.
Skin Injuries or Inflammation
Skin injuries, whether from acne, eczema, or other inflammatory conditions, can lead to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH). After the skin heals, darker patches may remain where the inflammation occurred, particularly in individuals with darker skin tones. This condition is often more pronounced in areas that have experienced significant trauma or irritation.
Understanding the connection between skin injuries and pigmentation is essential for developing effective treatment strategies. Preventive measures, such as using non-comedogenic skincare products, can help minimize the risk of acne and subsequent hyperpigmentation. Treatments for PIH may include topical agents, chemical peels, and laser therapy to promote even skin tone and reduce the appearance of dark spots.
By recognizing the various causes of pigmentation, individuals can better address their specific concerns and work towards effective treatment options. Understanding these factors also helps healthcare providers create personalized plans that consider an individual’s unique skin type and history.
Can Pigmentation Be Cured Permanently?
The core question of this article is whether pigmentation can be cured permanently. Understanding the nature of different types of pigmentation is crucial to addressing this question. While many treatments are available, their effectiveness can vary based on individual circumstances, including skin type, underlying causes, and adherence to treatment protocols. This section will explore the various types of pigmentation and the prospects for permanent solutions.
Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation is characterized by darkened patches on the skin resulting from excess melanin production. It can occur due to various factors such as sun exposure, hormonal changes, and skin injuries. Addressing hyperpigmentation often requires a multifaceted approach.
Treatment Options
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are commonly prescribed for hyperpigmentation and can effectively reduce dark spots over time. Key ingredients include:
- Hydroquinone: A skin-lightening agent that inhibits melanin production. It is often recommended for short-term use due to potential side effects.
- Retinoids: These vitamin A derivatives promote cell turnover and help fade dark spots. Consistent use can lead to improved skin texture and tone.
- Vitamin C: An antioxidant that brightens the skin and reduces pigmentation. It can be combined with other treatments for enhanced effects.
However, maintaining results often requires ongoing use of these medications, as stopping treatment can lead to a resurgence of pigmentation.
To learn more about them you can read more from our page on Treatments for Hyperpigmentation.
Professional Treatments
For individuals seeking more immediate or pronounced results, professional treatments may be beneficial:
- Laser Therapy: This technique uses focused light to target pigmented areas, breaking down melanin and promoting even skin tone. Different types of lasers are used based on the depth and nature of pigmentation. You can explore different laser opportunities at derma advance services page.
- Chemical Peels: By applying a chemical solution to the skin, superficial layers are exfoliated, allowing new, less pigmented skin to surface. This treatment can also improve skin texture and minimize fine lines.
While these professional treatments can provide significant improvement, they often need to be repeated periodically to maintain long-term effects.
Can Hyperpigmentation Be Cured Permanently?
While treatments can significantly reduce hyperpigmentation, several factors can influence the likelihood of recurrence. Sun exposure remains a leading cause of hyperpigmentation; therefore, diligent sun protection is essential for anyone undergoing treatment. Additionally, hormonal changes, such as those experienced during pregnancy or with hormonal therapies, can trigger the return of pigmentation. Thus, while not always permanent, effective management is possible through a combination of treatments and preventive measures.
Hypopigmentation
Hypopigmentation refers to areas of skin that are lighter than the surrounding skin, often resulting from a reduction in melanin. Conditions such as vitiligo and albinism fall under this category. Treatment approaches for hypopigmentation focus primarily on management rather than permanent cures.
Treatment Options
Camouflage Treatments
For conditions like vitiligo, camouflage makeup can be an effective solution. This type of makeup is designed to blend with the surrounding skin, providing a more uniform appearance. While it can improve the aesthetic aspect of hypopigmentation, these solutions are not permanent cures and require regular application.
Repigmentation Therapies
Some treatments aim to stimulate melanin production in depigmented areas:
- Light Therapy: Treatments such as narrowband UVB phototherapy can stimulate the melanocytes in the skin to produce more melanin. However, results can vary widely among individuals.
- Topical Corticosteroids: These can reduce inflammation and may promote repigmentation in some cases, particularly when used in conjunction with other treatments.
Despite these options, achieving consistent and significant results can be challenging, and maintenance treatments are often needed to sustain any repigmentation achieved.
Can Hypopigmentation Be Cured Permanently?
Unfortunately, conditions like vitiligo often have no definitive cure. The focus of treatment typically revolves around management and cosmetic solutions rather than seeking permanent fixes. Patients are encouraged to explore options that enhance their skin’s appearance and boost their confidence while accepting that complete restoration of skin color may not be feasible.
In summary, while many treatments exist for both hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation, the prospect of permanent cures varies significantly based on individual circumstances. Ongoing management and protective measures are essential for achieving the best possible outcomes in pigmentation treatment.
Factors Influencing the Permanence of Pigmentation Treatment
When it comes to treating pigmentation, various factors can influence the effectiveness and permanence of the results. Understanding these factors is crucial for individuals seeking long-lasting solutions to pigmentation issues. In this section, we will explore the key elements that can impact the outcomes of pigmentation treatments.
Type of Pigmentation
The specific type of pigmentation plays a significant role in how effectively it can be treated and whether the results can be permanent. Here are some key points to consider:
- Hyperpigmentation: Conditions like melasma and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation may respond differently to treatment. Melasma, often triggered by hormonal changes, can be particularly challenging, as it may recur with hormonal fluctuations or sun exposure. On the other hand, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation may fade more quickly with appropriate treatments.
- Hypopigmentation: Conditions such as vitiligo often require ongoing management rather than definitive cures. Treatments aimed at repigmentation can be effective, but results may vary widely among individuals, making it challenging to achieve permanent results.
Ultimately, understanding the type of pigmentation can help set realistic expectations for treatment outcomes and guide the choice of appropriate therapies.
Skin Type and Response to Treatment
Individual skin characteristics greatly influence how treatments work and how the skin reacts. Key factors include:
- Skin Type: Different skin types (oily, dry, combination, or sensitive) can react variably to treatments. For example, individuals with sensitive skin may experience irritation or adverse reactions to certain topical agents, potentially affecting the treatment’s efficacy.
- Ethnicity: Skin color and ethnicity can also impact how pigmentation treatments work. For instance, individuals with darker skin tones may be more prone to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and may require more cautious approaches to treatments like lasers or chemical peels to avoid further pigmentation issues.
- Overall Health: A person’s overall health, including hormonal balance and skin conditions, can influence treatment response. Those with underlying health issues may find their pigmentation more challenging to treat effectively.
Understanding your skin type and how it interacts with different treatments can help individuals make informed choices and enhance their chances of achieving lasting results.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle choices play a crucial role in maintaining the results of pigmentation treatments and preventing recurrence. Important considerations include:
- Sun Protection: Exposure to UV radiation is a leading cause of pigmentation changes. Using broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher and reapplying it regularly can protect the skin from harmful rays and prevent new pigmentation from developing.
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in antioxidants can support skin health and aid in the healing process. Foods high in vitamins C and E, along with omega-3 fatty acids, can promote healthy skin and potentially reduce pigmentation.
- Skincare Routines: Consistent skincare practices, including the use of gentle cleansers, exfoliants, and hydrating products, can help maintain treatment results. Incorporating active ingredients like retinoids and vitamin C can further enhance skin renewal and brighten the complexion.
- Avoiding Triggers: For individuals prone to conditions like melasma, avoiding known triggers such as hormonal fluctuations, heat, and certain medications can help maintain results.
By making informed lifestyle choices, individuals can enhance the effectiveness of their pigmentation treatments and work toward more permanent solutions.
In conclusion, achieving permanent results in pigmentation treatment is influenced by multiple factors, including the type of pigmentation, individual skin characteristics, and lifestyle choices. Understanding these factors allows individuals to take a proactive approach in their treatment journey, leading to better outcomes and improved skin health.
Preventive Measures for Pigmentation
Preventing pigmentation is often more effective than treating it after it occurs. By adopting proactive measures, individuals can protect their skin from developing pigmentation issues and maintain an even skin tone. This section explores key preventive strategies to consider.
Sun Protection
One of the most critical steps in preventing pigmentation is protecting the skin from harmful UV rays. Prolonged sun exposure can exacerbate existing pigmentation and lead to new dark spots forming. Here’s how to ensure adequate sun protection:

- Daily Use of Sunscreen: Using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 is essential. Apply it generously to all exposed skin, even on cloudy days, and reapply every two hours, especially after swimming or sweating. Look for sunscreens that contain physical blockers like zinc oxide or titanium dioxide, as they provide excellent protection against UVA and UVB rays.
- Seek Shade: Whenever possible, stay in the shade, especially during peak sun hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.). This can significantly reduce sun exposure and the risk of pigmentation issues.
- Wear Protective Clothing: In addition to sunscreen, consider wearing wide-brimmed hats, long-sleeved shirts, and sunglasses to shield your skin from direct sunlight. Clothing with UPF (Ultraviolet Protection Factor) can provide additional defense against UV radiation.
- Be Mindful of Reflective Surfaces: Remember that UV rays can reflect off surfaces such as water, sand, and concrete. Taking extra precautions in these environments is crucial.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
In addition to sun protection, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can contribute significantly to skin health and help mitigate pigmentation issues. Consider the following:
- Balanced Diet: A diet rich in antioxidants can combat oxidative stress and promote skin health. Include plenty of fruits and vegetables, especially those high in vitamins C and E, as they can help brighten the skin and reduce pigmentation. Foods like berries, citrus fruits, nuts, and leafy greens are excellent choices.
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration is vital for overall skin health. Drinking plenty of water helps maintain skin elasticity and can aid in the healing process. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water daily, and adjust based on activity level and climate.
- Avoid Processed Foods: Limit the intake of processed foods high in sugar and unhealthy fats, as they can lead to inflammation and skin issues, potentially worsening pigmentation.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity promotes circulation and can enhance skin health. Exercise helps deliver oxygen and nutrients to the skin, contributing to a more radiant complexion.
Regular Skin Care Routine
Implementing a consistent skincare routine can help maintain an even skin tone and prevent new pigmentation from forming. Key elements of an effective skincare regimen include:
- Gentle Cleansing: Use a mild cleanser that suits your skin type to remove impurities without stripping natural oils. Cleansing twice daily can help prevent clogged pores and maintain healthy skin.
- Exfoliation: Regular exfoliation helps remove dead skin cells, promoting skin renewal and a brighter complexion. Incorporate gentle exfoliants like alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta-hydroxy acids (BHAs) into your routine, but avoid over-exfoliating, which can irritate the skin.
- Brightening Agents: Incorporate products that contain ingredients like vitamin C, niacinamide, or licorice extract, known for their brightening properties. These ingredients can help reduce existing pigmentation and prevent new spots from forming.
- Moisturizing: Keeping the skin well-hydrated is essential for overall skin health. Use a moisturizer suited to your skin type to maintain skin barrier function and prevent dryness, which can worsen pigmentation.
- Regular Dermatological Check-ups: Schedule regular visits with a dermatologist to monitor your skin’s health and address any concerns promptly. Professional guidance can help tailor your skincare routine to your specific needs and address any emerging pigmentation issues effectively.
By implementing these preventive measures, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of pigmentation and maintain healthier, more even-toned skin. Taking proactive steps today can lead to lasting benefits for the skin in the long run.
When to Seek Professional Help
Understanding when to consult a dermatologist is essential for managing pigmentation effectively. While many pigmentation issues can be addressed with over-the-counter treatments and lifestyle changes, certain situations warrant professional evaluation and intervention. This section discusses key indicators that suggest it may be time to seek expert help.
Sudden Changes in Pigmentation
Any sudden or significant change in your skin’s pigmentation should be taken seriously. This could include:
- New Dark Spots: The appearance of new dark spots or patches on the skin, particularly if they develop quickly or are larger than existing spots, could indicate an underlying issue that needs professional assessment.
- Changes in Existing Spots: If an existing mole or dark spot changes in size, shape, or color, this can be a warning sign of potential skin cancer. It’s important to have any such changes evaluated by a dermatologist.
- Spread of Pigmentation: If pigmentation spreads rapidly across different areas of the body, it may signal an underlying health condition that requires medical attention.
Worsening of Pigmentation
If you notice that your pigmentation is becoming more pronounced or resistant to at-home treatments, this could indicate that professional intervention is necessary. Signs include:
- Resistance to Treatment: If over-the-counter treatments or home remedies aren’t yielding results after a reasonable period, a dermatologist can provide access to stronger, prescription-grade treatments that may be more effective.
- Recurring Pigmentation: If pigmentation keeps coming back even after treatment, a healthcare professional can help identify the underlying causes and recommend a more effective treatment plan.
Underlying Skin Conditions
Sometimes, pigmentation issues are a symptom of an underlying skin condition that requires diagnosis and treatment. If you experience any of the following, it’s advisable to consult a dermatologist:
- Skin Irritation or Inflammation: Conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, or dermatitis can lead to pigmentation changes. A dermatologist can provide a proper diagnosis and treatment to address both the underlying condition and the pigmentation.
- Infectious Conditions: Infections like fungal or bacterial infections may also cause pigmentation changes. Timely treatment can prevent further complications.
Seeking Guidance for Cosmetic Procedures
If you are considering more aggressive treatments for pigmentation, such as laser therapy, chemical peels, or microdermabrasion, it’s important to consult a dermatologist first. They can:
- Assess Your Skin Type: Different skin types react differently to various treatments. A dermatologist can evaluate your skin and recommend the most appropriate procedure for your specific condition.
- Discuss Potential Risks: Professional guidance is essential to understanding the risks and benefits of treatments, as well as what to expect during recovery.
- Provide a Comprehensive Treatment Plan: A dermatologist can develop a tailored plan that incorporates multiple treatment modalities, lifestyle changes, and skincare routines for optimal results.
Regular Skin Check-ups
Even if you do not currently have pigmentation issues, regular skin check-ups with a dermatologist can be beneficial. These visits can help:
- Monitor Changes: Regular check-ups can help track changes in your skin over time, allowing for early detection of any issues.
- Educate You on Prevention: Dermatologists can provide personalized advice on skincare routines and preventive measures tailored to your skin type.
- Address Other Skin Concerns: If you have other skin concerns such as acne, rosacea, or aging signs, a dermatologist can recommend effective treatments that do not conflict with your pigmentation management.
In conclusion, while many pigmentation issues can be managed at home, understanding when to seek professional help is crucial for achieving the best outcomes. Early intervention can lead to more effective treatment and help you maintain healthy, even-toned skin.
Conclusion
In summary, while pigmentation can often be effectively managed through various treatments, the possibility of a permanent cure varies greatly among individuals. Key factors influencing outcomes include the type of pigmentation, skin type, and personal lifestyle choices.
Understanding your specific pigmentation type is essential. For example, hyperpigmentation, caused by factors like sun exposure and hormonal changes, often responds well to treatments such as topical creams and professional therapies. In contrast, hypopigmentation conditions like vitiligo may require a different approach, focusing more on management and cosmetic solutions rather than a permanent fix.
Additionally, individual skin types react differently to treatments. Genetics, ethnicity, and overall skin health play crucial roles in determining how your skin responds. Therefore, tailoring treatment plans to suit individual needs is vital for optimal results.
Moreover, lifestyle choices significantly impact skin health and the effectiveness of pigmentation treatments. Regular sun protection, a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, and a consistent skincare routine can help maintain treatment results and prevent the recurrence of pigmentation issues.
At Derma Advance, we understand the complexities of pigmentation and offer comprehensive skin care solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our experienced dermatologists are committed to helping you achieve your desired skin tone and health through personalized treatment plans.
If you have any concerns about pigmentation or wish to explore effective treatment options, we encourage you to reach out to us. Contact us today for more information. To schedule a consultation, you can easily book an appointment with our specialists. We are here to help you on your journey to healthier, more radiant skin!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What causes pigmentation in the skin?
Pigmentation is primarily caused by an excess or deficiency of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color.
Common causes include genetic predisposition, prolonged sun exposure, hormonal changes (such as during pregnancy), and skin injuries or inflammation. Understanding these factors can help in managing pigmentation effectively.
Can pigmentation be cured permanently?
The potential for a permanent cure for pigmentation varies depending on the type.
While some forms of hyperpigmentation, like sunspots, can be effectively treated, others, such as melasma, may require ongoing management. Factors like skin type, lifestyle choices, and adherence to treatment plans play significant roles in determining the permanence of results.
What are the different types of pigmentation?
There are several types of pigmentation, primarily classified into hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation.
Hyperpigmentation includes conditions such as sunspots (caused by UV exposure), melasma (often linked to hormonal changes), and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (arising from skin trauma). Hypopigmentation includes conditions like vitiligo and albinism, characterized by a lack of melanin.
What treatments are available for pigmentation?
Treatments for pigmentation vary widely and include topical agents like hydroquinone, retinoids, and vitamin C, which can lighten dark spots.
Professional treatments such as chemical peels, laser therapy, and microdermabrasion can also significantly improve pigmentation issues. It’s essential to consult a dermatologist to determine the most suitable treatment plan.
How can I prevent pigmentation from worsening?
Preventive measures are crucial for managing pigmentation.
Daily use of broad-spectrum sunscreen is vital to protect against UV rays, which can worsen existing pigmentation. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, staying hydrated, and following a consistent skincare routine can help keep your skin healthy and minimize pigmentation issues.
Is it safe to use home remedies for pigmentation?
Many people explore home remedies for pigmentation, but their effectiveness and safety can vary.
Ingredients like lemon juice, turmeric, and aloe vera are popular but may not work for everyone and can sometimes cause skin irritation. It’s advisable to consult a dermatologist before starting any home treatment to ensure it won’t aggravate the condition.
When should I see a dermatologist for pigmentation concerns?
If you notice any sudden changes in your pigmentation, such as rapid darkening, new spots appearing, or changes in texture, it’s essential to seek professional advice.
Additionally, if over-the-counter treatments are ineffective after a reasonable period, consulting a dermatologist can provide tailored treatment options and help rule out underlying skin conditions.
How does skin type affect pigmentation treatment?
Skin type significantly impacts how pigmentation treatments work.
Individuals with darker skin tones may experience different responses to certain treatments compared to those with lighter skin. Factors such as skin sensitivity, ethnic background, and overall health can influence the effectiveness and safety of various treatments, making it crucial to have a personalized approach when addressing pigmentation issues.

