What is Sun Damage?
Sun damage refers to skin changes caused by prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or artificial sources like tanning beds. It includes sunburn, premature aging (photoaging), and increased risk of skin cancer.
Sun damage occurs when UV radiation penetrates the skin, damaging its cellular structure and causing various effects. Acute effects include sunburn, characterized by redness, pain, and sometimes blistering. Long-term exposure leads to photoaging, visible as wrinkles, sagging skin, and uneven pigmentation.
UV radiation also increases the risk of skin cancer, including basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. Prevention is crucial, including sunscreen use, protective clothing, and avoiding peak sun exposure hours. Treatments for sun damage range from topical creams and laser therapies to surgical procedures for skin cancer removal.
Immense Care
We aim to provide immense care tailored to manage and treat your health condition. Be assured, you are in safe hands!
Modern Techniques
We provide modern treatments to ensure you get the quickest and most effective solution to your health conditions!
Symptoms of Sun Damage
What are the Symptoms of Sun Damage?
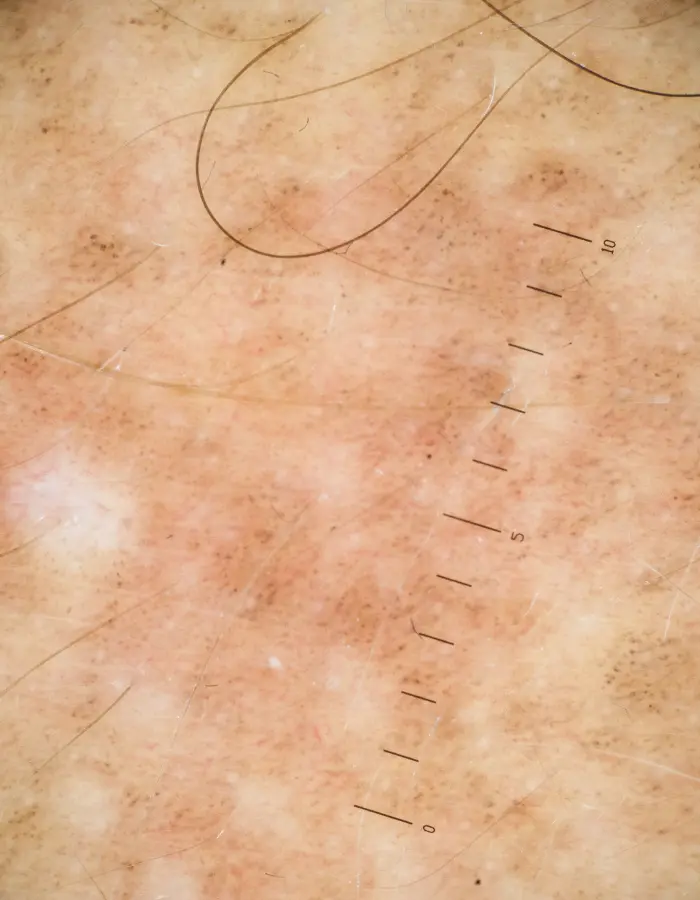
Symptoms of sun damage vary depending on the severity and duration of UV exposure. Acute sun damage presents as sunburn, characterized by redness, pain, and in severe cases, blistering. Chronic sun exposure leads to photoaging, visible as fine lines, wrinkles, sagging skin, and age spots (hyperpigmentation).
Long-term effects include an increased risk of skin cancer, with basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma appearing as new growths or changes in existing moles or lesions. Melanoma, the most serious form of skin cancer, may develop from new or existing moles and requires prompt medical attention.
Prevention involves sun protection measures such as wearing broad-spectrum sunscreen, protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses. Regular skin checks and early detection are essential for managing sun damage and preventing skin cancer.
Sunburn
Redness, pain, and sometimes blistering of the skin caused by excessive UV exposure, typically appearing several hours after sun exposure.
Photoaging
Visible signs of aging caused by long-term UV exposure, including wrinkles, sagging skin, and uneven pigmentation.
Hyperpigmentation
Dark spots or patches on the skin caused by an increase in melanin production in response to UV exposure.
Skin Cancer Risk
Increased likelihood of developing skin cancer due to cumulative UV damage, including basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
Actinic Keratosis
Rough, scaly patches on the skin caused by prolonged sun exposure, considered precancerous and requiring medical evaluation.
Eye Damage
UV radiation can cause eye damage, including cataracts, macular degeneration, and photokeratitis (sunburn of the eye).
Diagnosis of Sun Damage
1
Visual Examination
A dermatologist assesses sun-damaged skin, looking for signs of photoaging, sunspots, and changes in skin texture.
2
Dermatoscopy
Dermatoscopy magnifies skin lesions, allowing for a detailed examination of their structure and characteristics, aiding in the diagnosis of skin cancer.
3
Skin Biopsy
A biopsy involves removing a small sample of skin for laboratory analysis, confirming the presence of abnormal cells or skin cancer caused by sun exposure.
4
Imaging Techniques
Imaging technologies like ultrasound or dermoscopy help evaluate deeper skin layers and assess the extent of sun damage or skin cancer involvement.
5
Patient History
Reviewing the patient's history of sun exposure, sun protection practices, and previous skin conditions provides valuable insights into their risk of sun damage and skin cancer.
6
Differential Diagnosis
Considering other skin conditions, such as eczema, psoriasis, or fungal infections, helps ensure an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan for sun-damaged skin.
Book Your Appointment
Find Solution to Sun Damage Now!
Meet Our Expert Sun Damage Specialists


Treatment of Sun Damage
How is Sun Damage treated?
Treatment options for sun damage aim to repair existing damage and prevent future complications. Topical treatments such as retinoids and antioxidants help reverse photoaging by stimulating collagen production and reducing pigmentation.
Laser therapies target specific skin concerns, including wrinkles, sunspots, and vascular changes caused by sun damage. Procedures like laser resurfacing and intense pulsed light (IPL) therapy promote skin renewal and even skin tone.
Surgical interventions may be necessary for skin cancers resulting from sun exposure. These include excisional surgery to remove cancerous growths and Mohs surgery for precise removal of skin cancer layers while preserving healthy tissue.
Topical Treatments
Products containing retinoids and antioxidants help repair sun-damaged skin by boosting collagen production and reducing pigmentation.
Laser Therapy
Laser treatments target sun damage, including wrinkles, sunspots, and uneven skin tone, promoting collagen synthesis and skin renewal.
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels exfoliate the skin’s outer layer, reducing sunspots, fine lines, and uneven texture caused by UV damage.
Cryotherapy
Cold therapy is used to freeze and destroy abnormal skin cells, such as actinic keratosis, caused by sun exposure.
Photodynamic Therapy (PDT)
PDT uses light-sensitive medication and specific light wavelengths to target and destroy abnormal cells, including precancerous lesions.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical procedures, such as excisional surgery and Mohs surgery, remove skin cancers caused by prolonged sun exposure while preserving healthy tissue.
Causes of Sun Damage
1
Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation
UV radiation from the sun penetrates the skin, damaging DNA and triggering cellular changes that can lead to sunburn, photoaging, and skin cancer.
2
UVA vs. UVB
UVA rays penetrate deeper into the skin, causing long-term damage like wrinkles and age spots, while UVB rays primarily cause sunburn and skin cancer.
3
Tanning Beds
Artificial sources of UV radiation, such as tanning beds and sunlamps, emit high levels of UV rays that contribute to premature skin aging and skin cancer risk.
4
Sun Exposure Patterns
Prolonged or intense sun exposure, especially during outdoor activities or vacations, increases the cumulative damage to the skin and risk of sunburn and skin cancer.
5
Geographic Location
Geographic factors, such as proximity to the equator or high-altitude regions, influence UV intensity and exposure levels, impacting sun damage risk.
6
Skin Type and Pigmentation
Individuals with fair skin, light hair, and freckles have less natural protection against UV radiation, increasing their susceptibility to sun damage and skin cancer.
How to Prevent Sun Damage?
Sun damage refers to skin changes caused by prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or artificial sources like tanning beds. It includes sunburn, premature aging (photoaging), and increased risk of skin cancer.
Sun damage prevention is essential for maintaining healthy skin and reducing the risk of skin cancer. Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher daily, even on cloudy days, and reapply every two hours or after swimming or sweating. Seek shade during peak sun hours, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., when UV radiation is strongest.
Wear protective clothing, including wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses with UV protection, and long sleeves and pants. Regular skin checks and annual dermatology visits can detect early signs of sun damage and skin cancer, ensuring timely treatment and management.