What is Melasma?
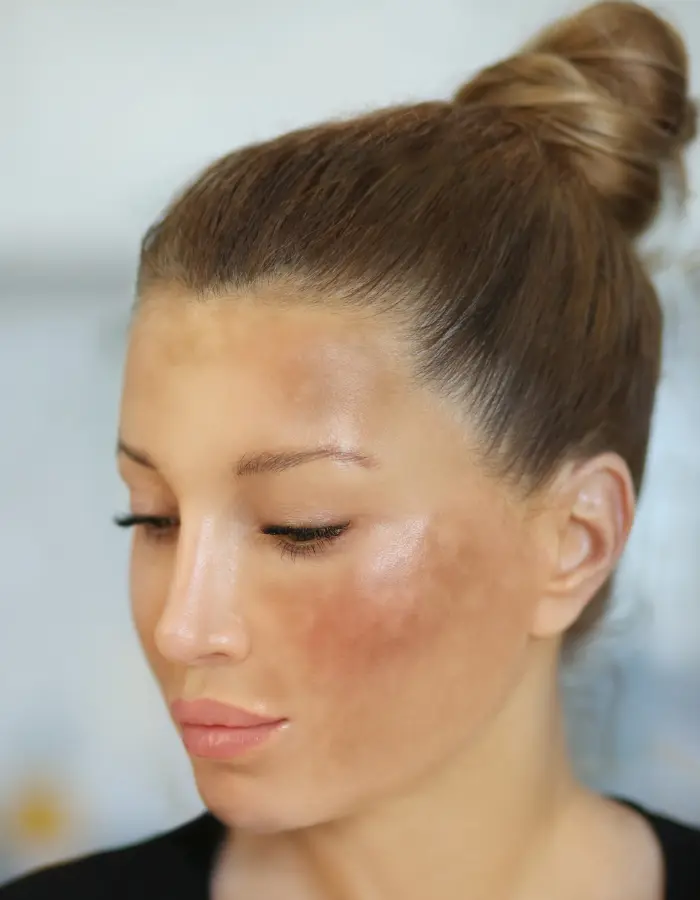
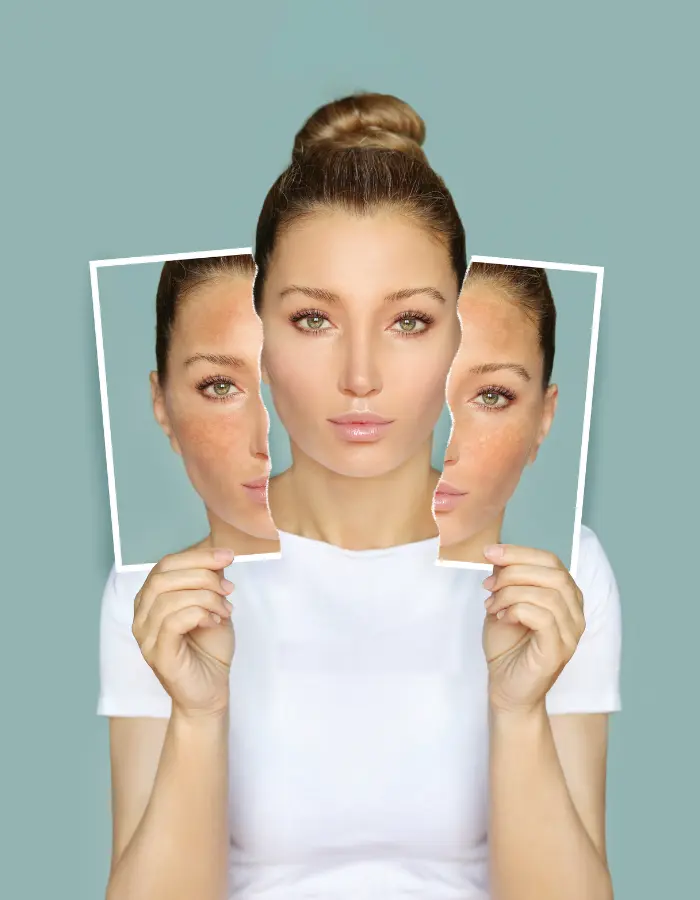
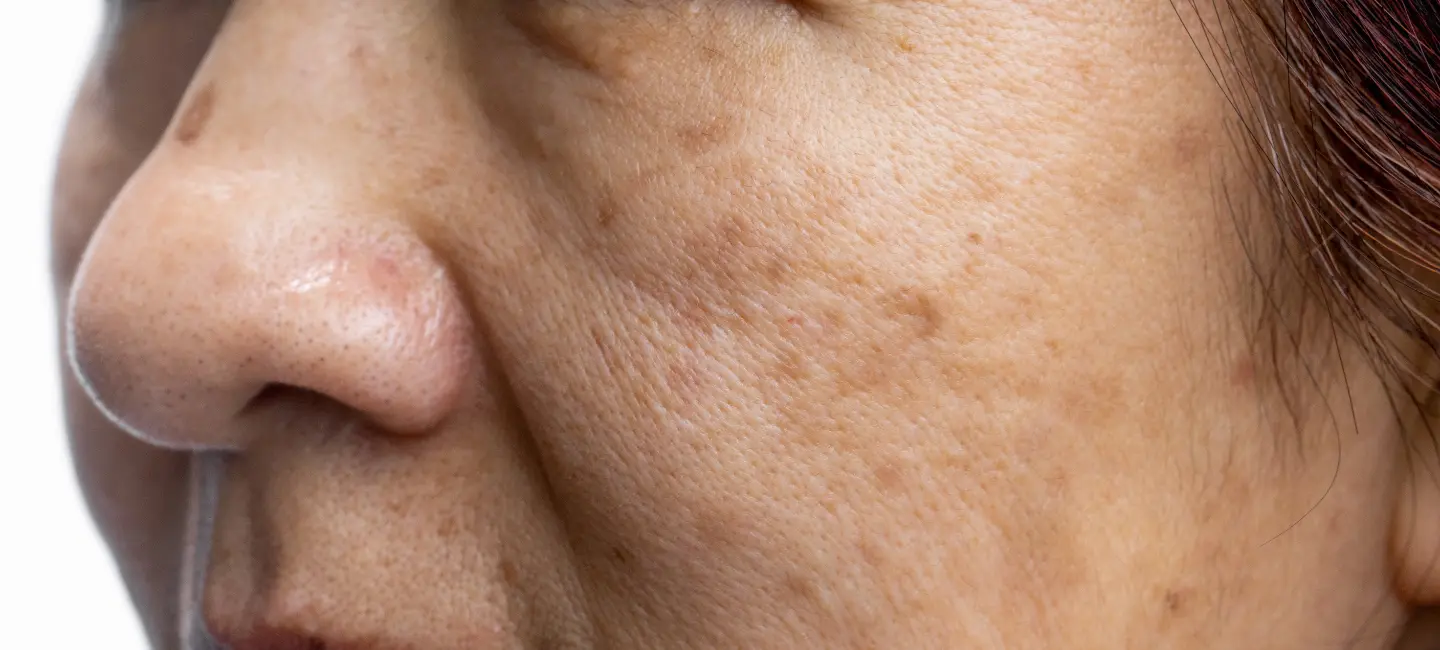
Melasma is a skin condition marked by dark, blotchy patches on the face, usually due to hormonal changes. It's common during pregnancy or with oral contraceptive use.
Melasma results from an overproduction of melanin, leading to dark patches primarily on the face. This condition is often triggered by hormonal fluctuations, such as those occurring during pregnancy or from using birth control pills. Sun exposure exacerbates the condition, making the patches more noticeable.
Treatments for melasma include topical creams, chemical peels, and laser therapy. It’s important to protect the skin from the sun and follow a dermatologist's advice for effective management. While melasma can be persistent, proper treatment can significantly reduce its appearance.
Immense Care
We aim to provide immense care tailored to manage and treat your health condition. Be assured, you are in safe hands!
Modern Techniques
We provide modern treatments to ensure you get the quickest and most effective solution to your health conditions!
Symptoms of Melasma
What are the Symptoms of Melasma?
Symptoms of melasma include dark, irregularly shaped patches on the face, particularly on the cheeks, forehead, nose, and upper lip. These patches are usually symmetrical and can vary in color from light brown to dark brown or gray.
Melasma is typically asymptomatic, meaning it doesn't cause physical discomfort. However, it can have significant psychological effects, impacting an individual’s self-esteem and confidence. Early diagnosis and consistent treatment are crucial for managing the condition effectively.
Facial Dark Patches
Dark, blotchy patches typically appear on the cheeks, forehead, nose, and upper lip, with a symmetrical pattern.
Cheek Hyperpigmentation
The cheeks are a common area for melasma, where dark patches may form due to hormonal changes and sun exposure.
Forehead Discoloration
The forehead can develop dark patches, often worsened by sun exposure, forming a characteristic ‘mask-like’ appearance.
Upper Lip Pigmentation
Melasma can cause dark spots on the upper lip, which can resemble a mustache, often aggravated by sun exposure.
Symmetrical Patches
Melasma often presents as symmetrical patches, meaning both sides of the face are affected equally, a distinguishing feature of this condition.
Neck and Forearm Spots
In some cases, melasma can also affect sun-exposed areas like the neck and forearms, leading to dark patches.
Diagnosis of Melasma
1
Physical Examination
A dermatologist will assess the affected areas for characteristic dark patches, examining their color, shape, and distribution.
2
Medical History Review
Reviewing your medical history helps identify potential triggers like hormonal changes or medication use contributing to melasma.
3
Wood's Lamp Examination
This test involves using ultraviolet light to examine the skin, helping to determine the depth and extent of pigmentation.
4
Biopsy
In rare cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to rule out other conditions and confirm the diagnosis of melasma.
5
Hormonal Assessment
An evaluation of hormonal levels may be conducted to identify imbalances that could be causing or exacerbating melasma.
6
Sun Exposure History
Assessing your history of sun exposure helps determine if UV radiation is a contributing factor to melasma.
Book Your Appointment
Find Solution to Melasma Now!
Meet Our Expert Melasma Specialists


Treatment of Melasma
How is Melasma treated?
Melasma treatment focuses on reducing the appearance of dark patches and preventing further pigmentation. Topical creams containing hydroquinone, tretinoin, or corticosteroids are commonly used to lighten the skin. These treatments help reduce melanin production and promote skin cell turnover.
More intensive treatments, such as chemical peels and laser therapy, can be effective in breaking down melanin and rejuvenating the skin. Chemical peels use acids to exfoliate the skin, while laser therapy targets pigment deposits with light energy. It’s crucial to perform these treatments under professional guidance to avoid complications.
Sun protection is essential in treating melasma. Regular use of a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher helps prevent the condition from worsening. Protective clothing and avoiding direct sunlight during peak hours are also recommended. Consistent follow-up with a dermatologist ensures the best results in managing melasma.
Topical Creams
Creams containing hydroquinone, tretinoin, or corticosteroids help lighten dark patches by reducing melanin production.
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels use acids to exfoliate the top layers of the skin, promoting cell turnover and reducing pigmentation.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy targets and breaks down melanin deposits in the skin, helping to lighten dark patches effectively.
Microdermabrasion
Microdermabrasion is a minimally invasive procedure that exfoliates the skin, reducing the appearance of melasma by removing the outermost layer.
Sun Protection
Regular use of broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher helps prevent melasma from worsening and protects treated areas.
Oral Medications
In some cases, oral medications like tranexamic acid may be prescribed to reduce melasma by addressing the underlying hormonal or vascular factors.
Causes of Melasma
1
Hormonal Changes
Fluctuations in hormones, such as during pregnancy or from birth control, can trigger melasma, leading to dark patches on the skin.
2
Sun Exposure
UV radiation stimulates melanin production, making sun exposure a significant factor in the development and worsening of melasma.
3
Genetics
Genetic predisposition plays a role, as individuals with a family history of melasma are more likely to develop the condition.
4
Medications
Certain medications, including some oral contraceptives and anti-seizure drugs, can cause or worsen melasma due to their effect on hormone levels.
5
Skin Inflammation
Inflammation from skin injuries or conditions like acne can trigger melanin overproduction, leading to melasma.
6
Cosmetic Products
Some cosmetic products that irritate the skin can increase the risk of melasma, especially if they make the skin more sensitive to sunlight.
How to Prevent Melasma?
Melasma is a skin condition marked by dark, blotchy patches on the face, usually due to hormonal changes. It's common during pregnancy or with oral contraceptive use.
Prevention of melasma involves diligent sun protection using broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF. Wearing protective clothing and avoiding peak sunlight hours also reduce exposure.
Maintaining a healthy skincare routine, including gentle cleansing and moisturizing, helps keep the skin in optimal condition. It’s essential to manage hormonal changes under medical supervision and avoid triggers like harsh skin treatments. Early intervention can significantly reduce the risk of melasma.