What is Hyperpigmentation?
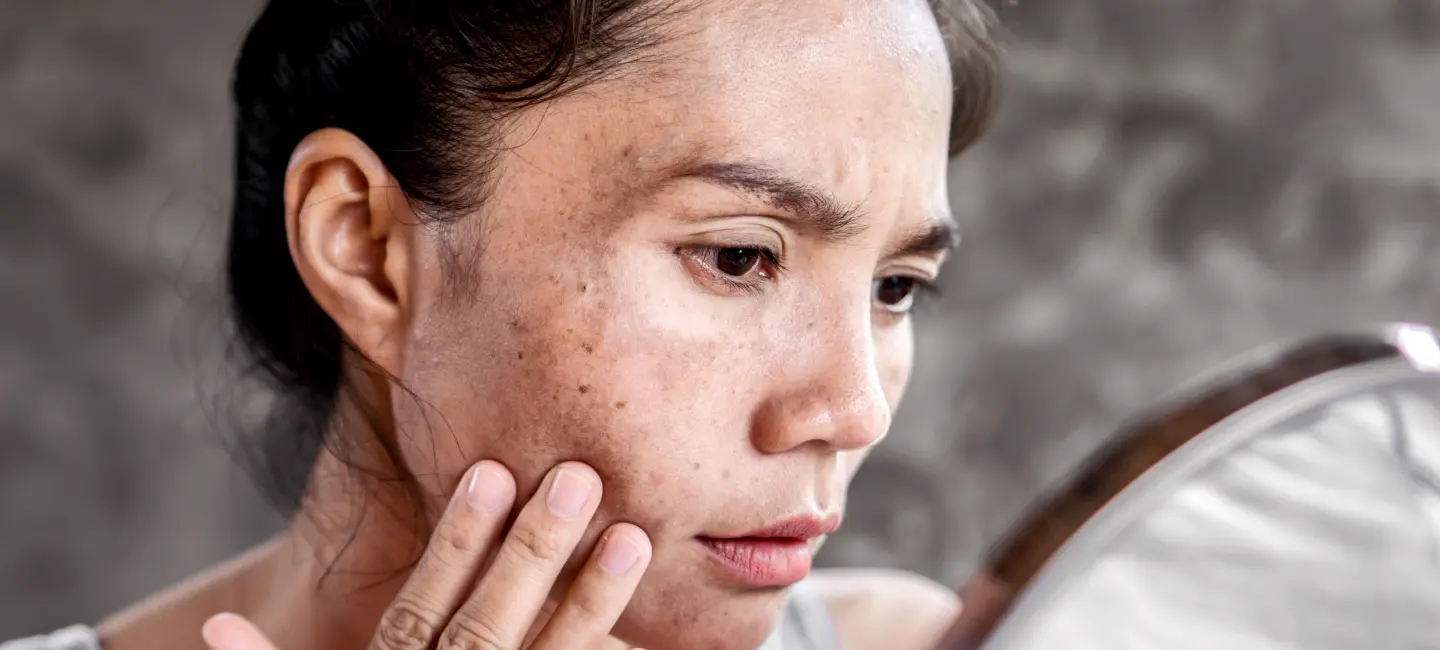
Hyperpigmentation is a condition where patches of skin become darker than surrounding areas due to excess melanin. It’s commonly caused by sun exposure, inflammation, or hormonal changes.
Hyperpigmentation results from an overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Common causes include excessive sun exposure, hormonal changes, and skin injuries. This condition can affect any skin type, but it’s more prevalent in individuals with darker skin tones.
Treatment options vary, including topical creams, laser therapy, and chemical peels. Addressing the underlying cause is crucial for effective treatment. Consulting a dermatologist can help identify the best approach for managing hyperpigmentation.
Immense Care
We aim to provide immense care tailored to manage and treat your health condition. Be assured, you are in safe hands!
Modern Techniques
We provide modern treatments to ensure you get the quickest and most effective solution to your health conditions!
Symptoms of Hyperpigmentation
What are the Symptoms of Hyperpigmentation?
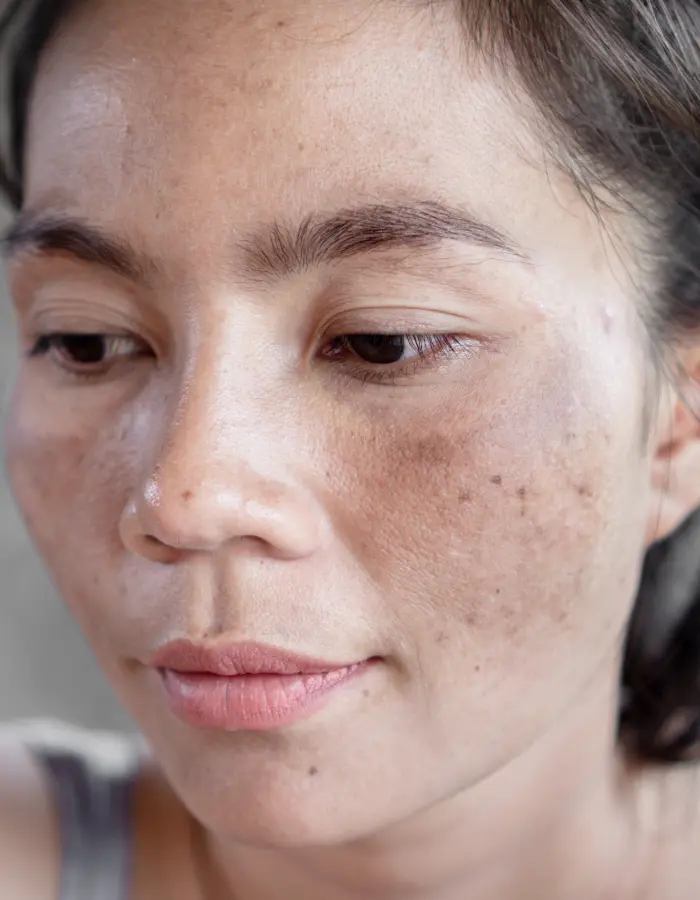
Hyperpigmentation manifests as dark patches or spots on the skin, typically appearing on the face, neck, hands, and other areas exposed to the sun. These patches vary in size and can be uniform or irregular in shape.
The condition often occurs due to factors like sun exposure, which stimulates melanin production, or hormonal changes such as those seen during pregnancy or with the use of oral contraceptives. Certain medications and skin injuries can also lead to hyperpigmentation.
Symptoms are generally cosmetic but may cause emotional distress. The dark spots can vary in color from light brown to black, depending on the individual’s skin tone and the severity of the condition. In some cases, the affected areas may feel rough or be prone to itching.
Freckles
Freckles are small, flat, tan or light brown spots caused by clusters of melanin, typically triggered by sun exposure. They commonly appear on sun-exposed areas like the face, arms, and shoulders.
Melasma
Melasma presents as larger, dark brown or grayish patches on the face, particularly on the cheeks, forehead, bridge of the nose, and upper lip. It is often exacerbated by hormonal changes such as pregnancy or birth control use, combined with sun exposure.
Post-inflammatory Hyperpigmentation
This type of hyperpigmentation occurs as a result of skin inflammation or injury, such as acne, eczema, or cuts. It manifests as darkened areas that persist after the initial skin condition has healed, due to excess melanin production during the healing process.
Solar Lentigines (Sun Spots)
Solar lentigines, commonly known as sun spots or age spots, are small, darkened patches of skin caused by prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays. They typically appear on areas of the body frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face, hands, shoulders, and back.
Drug-induced Hyperpigmentation
Drug-induced hyperpigmentation refers to darkening of the skin caused by certain medications or drugs. Examples include antimalarials, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and chemotherapy agents. The pigmentation changes can vary in intensity and distribution depending on the medication used.
Acanthosis Nigricans
Acanthosis nigricans is characterized by thick, darkened patches of skin with a velvety texture. These patches often occur in skin folds and creases, such as the neck, armpits, groin, and under the breasts. The condition is associated with insulin resistance, obesity, hormonal disorders, and certain medications.
Diagnosis of Hyperpigmentation
1
Physical Examination
During a physical examination, a dermatologist carefully inspects the affected areas, noting the color, size, and distribution of dark spots. This assessment helps determine the type and extent of hyperpigmentation present.
2
Medical History Review
A thorough review of your medical history is conducted to identify potential factors contributing to hyperpigmentation. This includes evaluating past and current medications, underlying health conditions, and previous skin treatments or procedures.
3
Additional Tests
Depending on the clinical presentation, further diagnostic tests such as a skin biopsy or Wood’s lamp examination may be recommended. These tests provide additional insights into the underlying causes of hyperpigmentation, ensuring an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
4
Dermatoscopy
Dermatoscopy involves using a handheld device with magnification and light to examine skin lesions more closely. This non-invasive technique helps dermatologists assess pigmented lesions and distinguish between different types of hyperpigmentation.
5
Photography Documentation
Photography documentation involves taking high-resolution photographs of the affected areas. These images serve as a visual record of the pigmentation patterns and can aid in monitoring changes over time and evaluating treatment effectiveness.
6
Patch Testing
Patch testing is used to identify specific allergens or irritants that may be triggering inflammatory hyperpigmentation, such as allergic contact dermatitis. This test involves applying small amounts of potential allergens to the skin under adhesive patches and observing any reactions.
Book Your Appointment
Find Solution to Hyperpigmentation Now!
Meet Our Expert Hyperpigmentation Specialists


Treatment of Hyperpigmentation
How is Hyperpigmentation treated?
Treating hyperpigmentation involves addressing the underlying cause and selecting the appropriate treatment. Topical treatments, including creams with ingredients like hydroquinone, retinoids, or vitamin C, are commonly used to lighten dark spots.
Advanced treatments such as laser therapy target specific areas of hyperpigmentation by breaking down melanin deposits. Chemical peels, which use acids to exfoliate the skin, can also reduce pigmentation by removing the top layers of skin.
It’s important to follow a dermatologist’s recommendations and to combine treatments with sun protection to prevent the condition from worsening. Regular application of sunscreen with high SPF is crucial in managing and preventing further hyperpigmentation.
Topical Creams
Topical creams containing ingredients like hydroquinone, retinoids (such as tretinoin), or vitamin C are effective in lightening dark spots. These creams work by reducing melanin production and promoting skin cell turnover, resulting in a more even skin tone.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy targets melanin deposits in the skin with high-energy light beams. This treatment breaks down pigmented cells and stimulates collagen production, helping to achieve a smoother and more uniform complexion. Multiple sessions are often necessary for optimal results.
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels involve applying a chemical solution to the skin, which causes controlled exfoliation of the outer layers. This process helps to remove pigmented cells and promote the growth of new, evenly pigmented skin. Peels can vary in strength (superficial to deep) and should be administered by a trained professional to minimize risks and maximize results.
Microdermabrasion
Microdermabrasion uses a minimally abrasive instrument to gently sand the skin, removing the thicker, uneven outer layer. This treatment can help improve the appearance of sun damage, age spots, and mild hyperpigmentation by stimulating skin regeneration.
Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) Therapy
IPL therapy uses broad-spectrum light to target melanin in the skin, breaking down dark spots and stimulating collagen production. It is effective for treating sun damage, age spots, and certain types of hyperpigmentation. Multiple sessions are usually required for best results.
Cosmetic Camouflage
Cosmetic camouflage involves using specially formulated makeup products to conceal hyperpigmented areas. These products are designed to provide long-lasting coverage and can be matched to the individual’s skin tone for a natural appearance. This method is non-invasive and offers immediate results.
Causes of Hyperpigmentation
1
Sun Exposure
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight stimulates melanin production in the skin, leading to the development of sun spots (solar lentigines) and freckles. Prolonged or intense sun exposure increases the risk of developing hyperpigmentation.
2
Hormonal Changes
Fluctuations in hormone levels, such as those occurring during pregnancy, menopause, or due to birth control use, can trigger hormonal changes that contribute to melasma. This type of hyperpigmentation typically appears as dark patches on the face.
3
Inflammation
Skin injuries or inflammatory conditions such as acne, eczema, or allergic reactions can lead to inflammation-induced hyperpigmentation. As the skin heals from these conditions, excess melanin production can result in dark spots or patches, known as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
4
Medications
Certain medications, such as antibiotics, antimalarials, and chemotherapy drugs, can increase skin sensitivity to sunlight (photosensitivity) or disrupt normal melanin production. This can lead to drug-induced hyperpigmentation, characterized by darkened patches on the skin.
5
Genetic Predisposition
Genetic factors can predispose individuals to developing hyperpigmentation. Certain ethnicities or family histories may increase susceptibility to conditions like melasma or freckles, particularly in response to environmental triggers like sun exposure.
6
Age-related Changes
As skin ages, changes in melanocyte activity and cumulative sun exposure can contribute to the development of age spots (lentigines) and other forms of hyperpigmentation. These pigmented lesions commonly appear on areas of the body exposed to the sun over time, such as the face, hands, and arms.
How to Prevent Hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation is a condition where patches of skin become darker than surrounding areas due to excess melanin. It’s commonly caused by sun exposure, inflammation, or hormonal changes.
Prevention of hyperpigmentation starts with protecting your skin from the sun by using broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher. Wearing protective clothing and avoiding peak sun hours can also help.
Regularly using gentle skincare products and avoiding skin injuries or irritation is crucial. Additionally, seeking early treatment for conditions like acne can prevent post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.