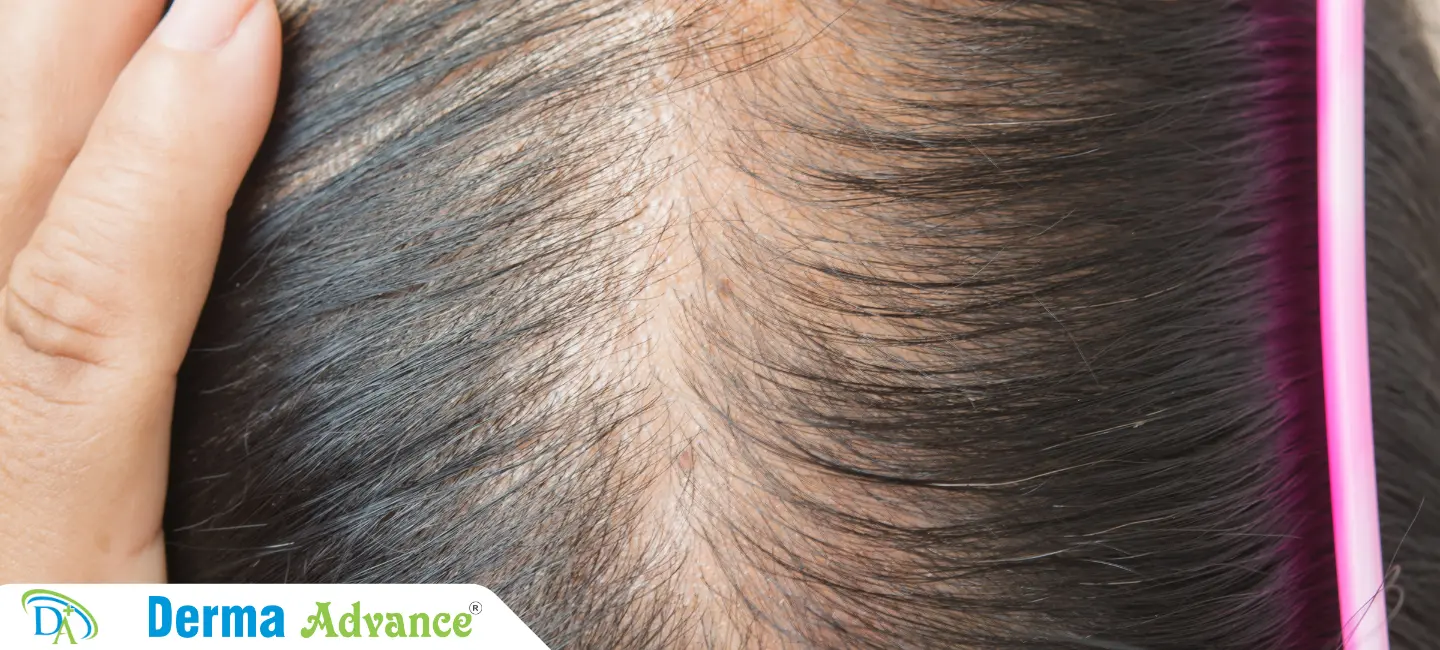
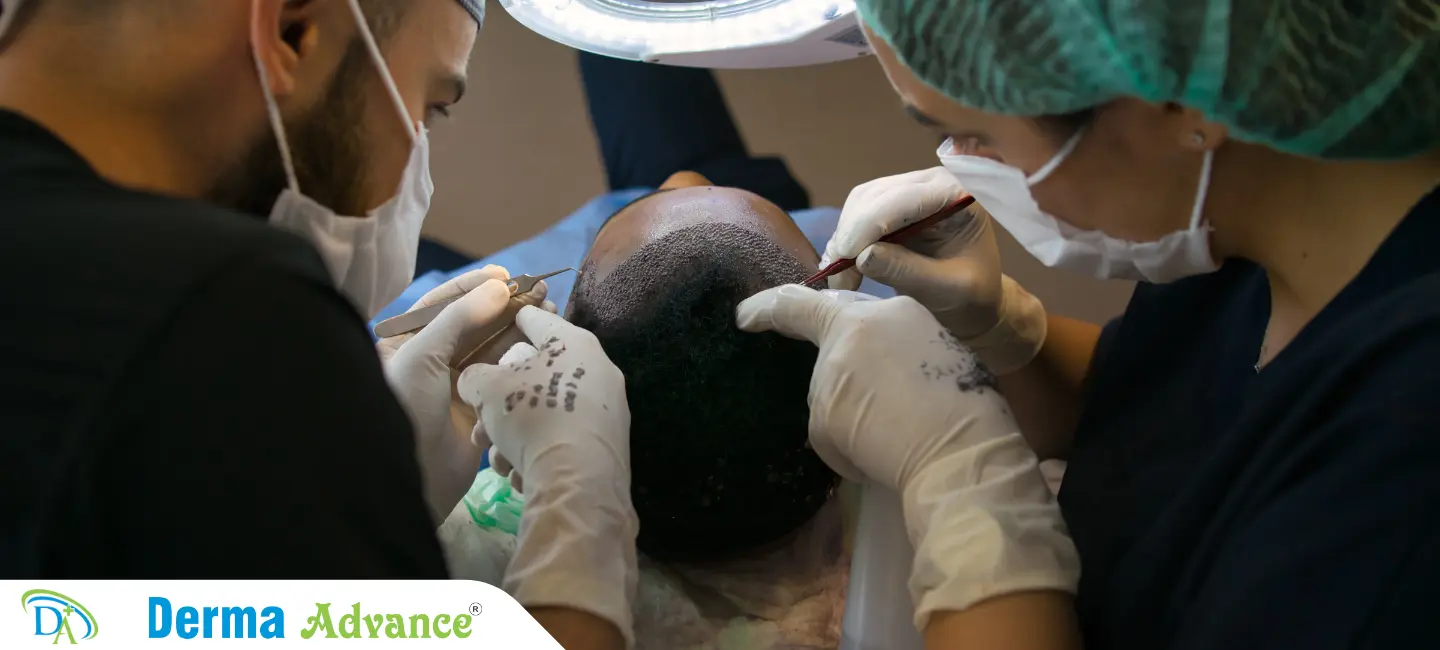
What is Hair Thinning?
Hair thinning refers to the gradual reduction in hair density and thickness, often influenced by genetic predisposition, hormonal changes, or scalp conditions.
Hair thinning involves progressive hair loss and decreased hair volume, impacting both men and women. Common causes include genetic factors (androgenetic alopecia), hormonal imbalances (e.g., thyroid disorders), and scalp conditions (e.g., alopecia areata).
Effective management strategies include topical treatments like minoxidil, oral medications, and advanced therapies such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections. Dermatological evaluation helps identify underlying causes and tailor treatment plans for optimal hair restoration.
Immense Care
We aim to provide immense care tailored to manage and treat your health condition. Be assured, you are in safe hands!
Modern Techniques
We provide modern treatments to ensure you get the quickest and most effective solution to your health conditions!
Symptoms of Hair Thinning
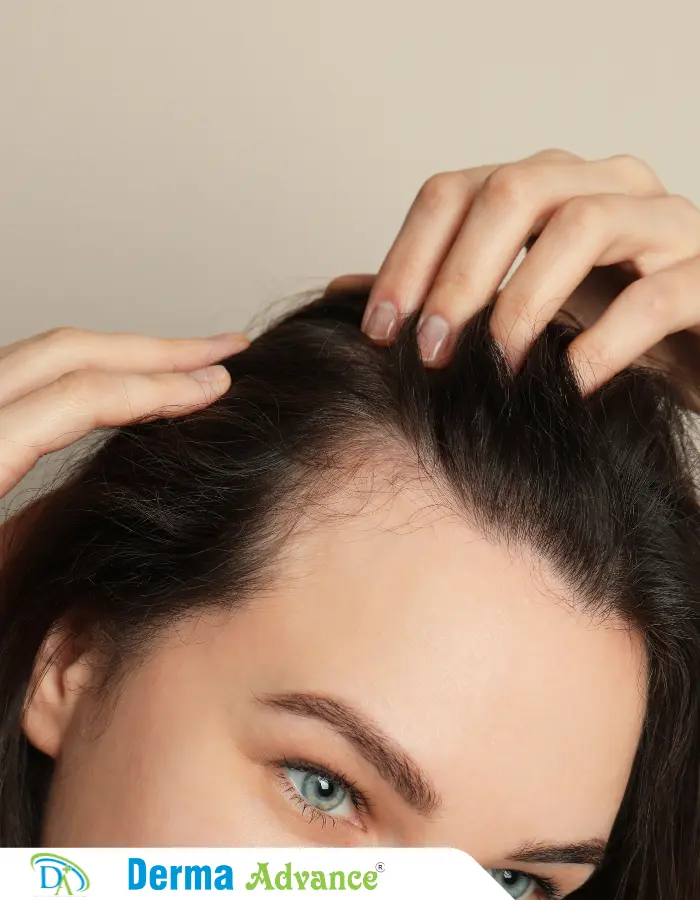
What are the Symptoms of Hair Thinning?
Hair thinning presents as increased hair shedding, noticeable scalp visibility, and reduced hair thickness, affecting hairstyle versatility and self-perception. Progressive hair loss may lead to scalp sensitivity or psychological distress, emphasizing the need for timely intervention.
Early symptoms include widening of the hair part, decreased hair density, and thinning along the crown or temples. Scalp examination helps assess hair follicle health and determine appropriate treatment strategies.
Personalized care involves combining topical treatments, nutritional supplements, and lifestyle modifications to promote hair growth and scalp health. Consultation with a dermatologist ensures comprehensive evaluation and management of hair thinning concerns.
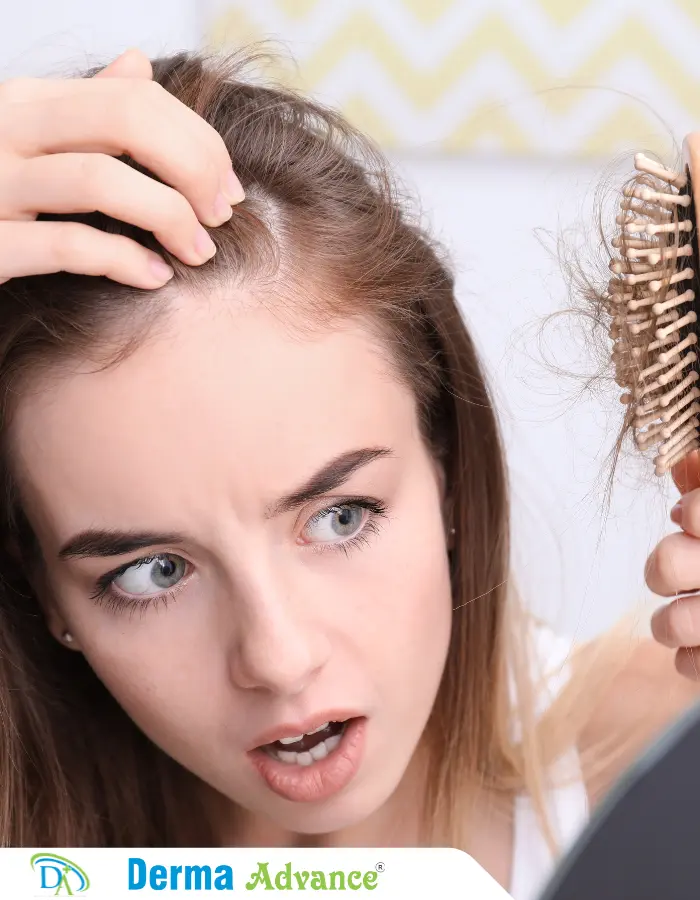
Increased Hair Shedding
Noticeable increase in daily hair shedding, indicating potential onset or progression of hair thinning and prompting early intervention.
Scalp Visibility
Greater visibility of the scalp due to reduced hair density or thinning, affecting hairstyle choices and personal appearance perception.
Reduced Hair Thickness
Decreased hair shaft diameter and texture changes, contributing to hair thinning and requiring targeted scalp and hair care interventions.
Scalp Sensitivity
Heightened scalp sensitivity or discomfort, associated with progressive hair thinning and influencing daily activities and hair care routines.
Psychological Impact
Emotional distress or self-esteem issues related to visible hair thinning, underscoring the importance of holistic hair care and psychological support.
Hair Part Widening
Widening of the hair part or visible scalp areas, indicating progressive hair loss and necessitating comprehensive evaluation and treatment.
Diagnosis of Hair Thinning
1
Hair Density Assessment
Evaluation of hair density changes or visible scalp areas, using standardized scales or visual inspection techniques to quantify hair thinning severity.
2
Scalp Condition Evaluation
Examination of scalp health indicators, including scalp oil production, inflammation levels, and follicle activity, guiding diagnostic criteria application and treatment recommendations.
3
Medical History Review
Comprehensive review of medical history, including family history of hair loss, hormonal imbalances, and scalp conditions influencing hair thinning progression and treatment planning.
4
Scalp Microscopic Analysis
Microscopic analysis of scalp tissue and hair follicles to identify cellular changes, microbial imbalances, or genetic factors contributing to hair thinning patterns and treatment responsiveness.
5
Differential Diagnosis Considerations
Differentiating hair thinning from other scalp conditions, such as alopecia areata or telogen effluvium, based on distinctive clinical features and diagnostic assessments to optimize treatment outcomes.
6
Scalp Health Assessment
Assessment of overall scalp health indicators, including hydration levels, barrier function, and sebum production, influencing hair follicle health and resilience against hair thinning.
Book Your Appointment
Find Solution to Hair Thinning Now!
Meet Our Expert Hair Thinning Specialists


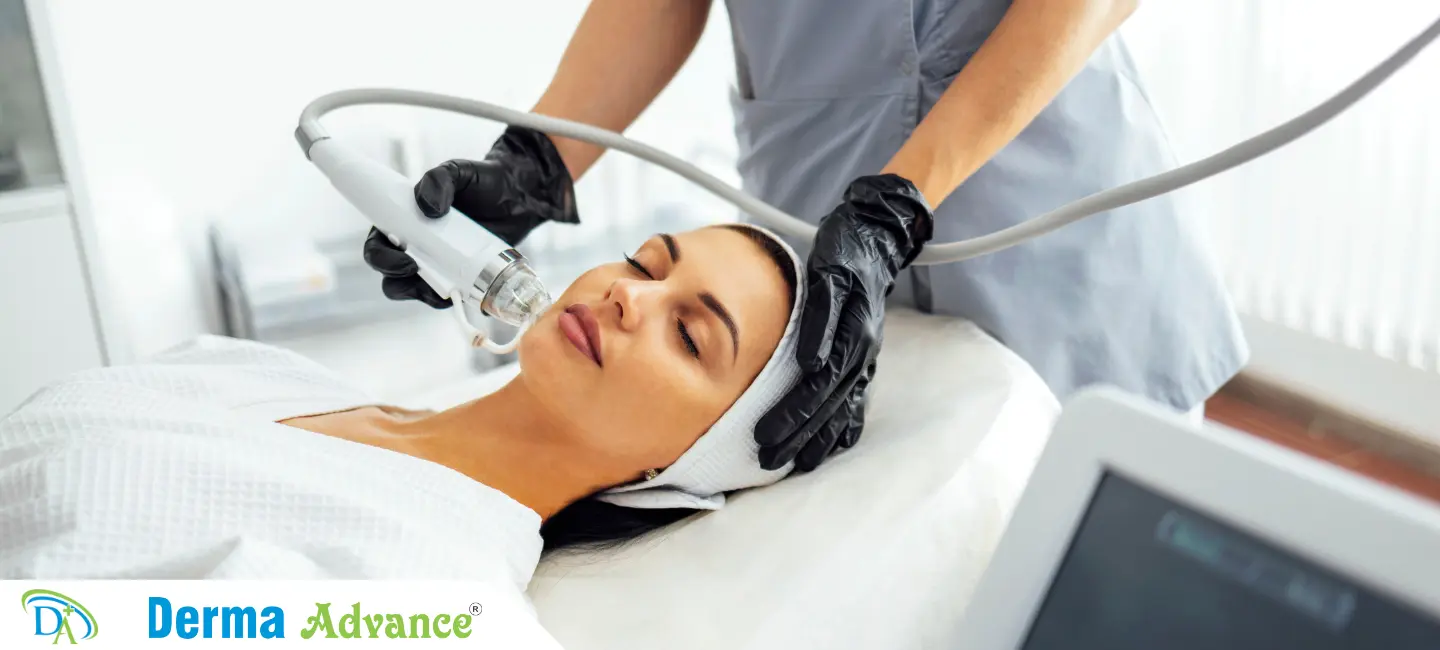
Treatment of Hair Thinning
How is Hair Thinning treated?
Treatment options for hair thinning include topical solutions like minoxidil to promote hair growth and improve follicle function. Oral medications such as finasteride may inhibit hair loss progression by blocking dihydrotestosterone (DHT) production.
Advanced therapies like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections harness growth factors to stimulate hair follicle activity and enhance hair density. Scalp microneedling and laser therapy offer non-invasive approaches to improve scalp circulation and support hair regrowth.
Comprehensive treatment plans integrate nutritional supplements, scalp care products, and lifestyle modifications to optimize hair health and minimize thinning. Dermatological consultation ensures personalized care tailored to individual hair loss patterns and treatment responses.
Topical Minoxidil
Application of minoxidil-based solutions to stimulate hair follicle growth and improve hair density, promoting scalp health and managing hair thinning.
Oral Medications
Use of medications like finasteride to inhibit DHT production and slow down hair loss progression, supporting long-term hair thinning management.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP)
PRP injections containing growth factors to rejuvenate hair follicles, enhance hair thickness, and stimulate natural hair regrowth in individuals experiencing hair thinning.
Scalp Microneedling
Micro-needling technique to improve scalp circulation, facilitate nutrient absorption, and promote hair follicle regeneration in patients with hair thinning.
Laser Therapy
Non-invasive laser treatments to enhance scalp health, reduce inflammation, and stimulate hair follicle activity for improved hair density and thickness.
Holistic Hair Care
Integration of nutritional supplements, scalp care routines, and stress management techniques to support overall hair health and manage hair thinning effectively.
Causes of Hair Thinning
1
Genetic Predisposition
Inherited genetic factors influencing hair follicle sensitivity to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), leading to progressive hair thinning and eventual hair loss.
2
Hormonal Imbalances
Fluctuations in hormone levels, such as androgens and thyroid hormones, affecting hair growth cycles and contributing to hair thinning patterns in men and women.
3
Scalp Conditions
Prevalence of scalp conditions like seborrheic dermatitis or scalp psoriasis, disrupting hair follicle function and exacerbating hair thinning symptoms.
4
Environmental Factors
Exposure to environmental stressors, pollutants, or UV radiation compromising scalp health and contributing to hair follicle miniaturization and increased hair shedding.
5
Nutritional Deficiencies
Inadequate intake of essential nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, and proteins, impairing hair follicle health and resilience against hair thinning in affected individuals.
6
Lifestyle Influences
Impact of lifestyle factors, including stress levels, dietary habits, and hair care practices, on hair growth cycles and susceptibility to hair thinning over time.
How to Prevent Hair Thinning?
Hair thinning refers to the gradual reduction in hair density and thickness, often influenced by genetic predisposition, hormonal changes, or scalp conditions.
Proactive scalp care includes using gentle shampoos, avoiding excessive heat styling, and incorporating nutrient-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and proteins into your diet to support hair growth.
Regular scalp massages and stress reduction techniques promote scalp circulation and enhance hair follicle health, minimizing the risk of hair thinning over time.