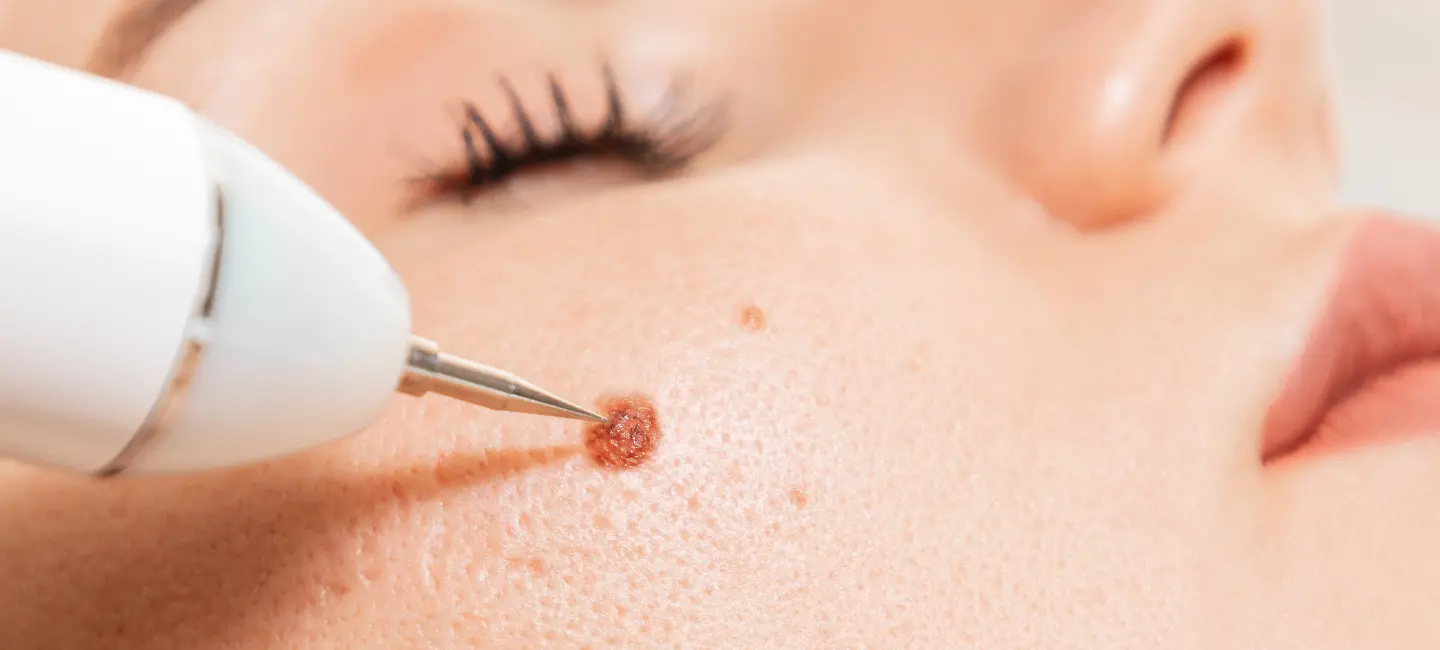
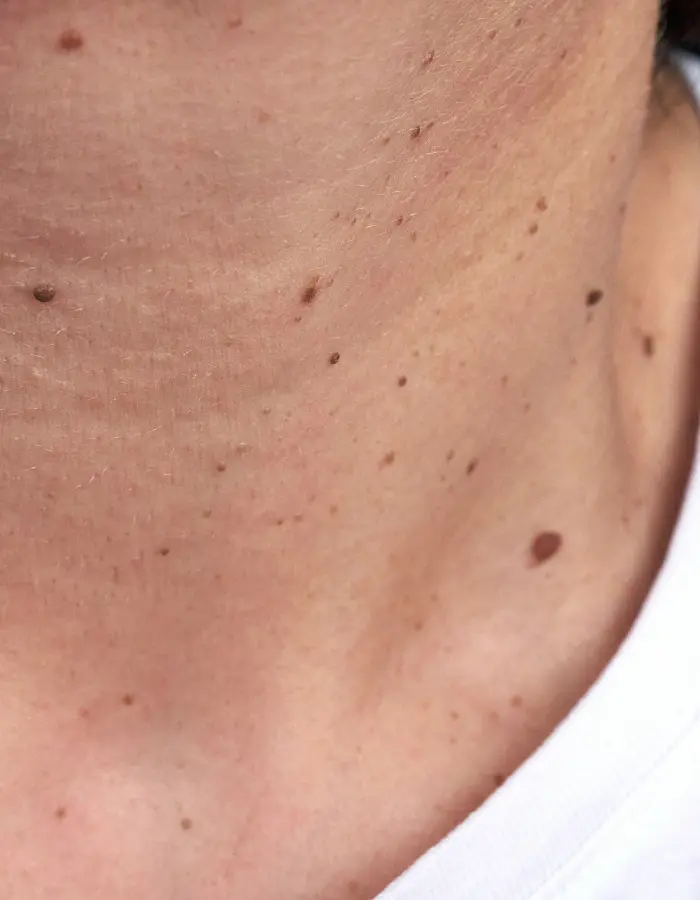
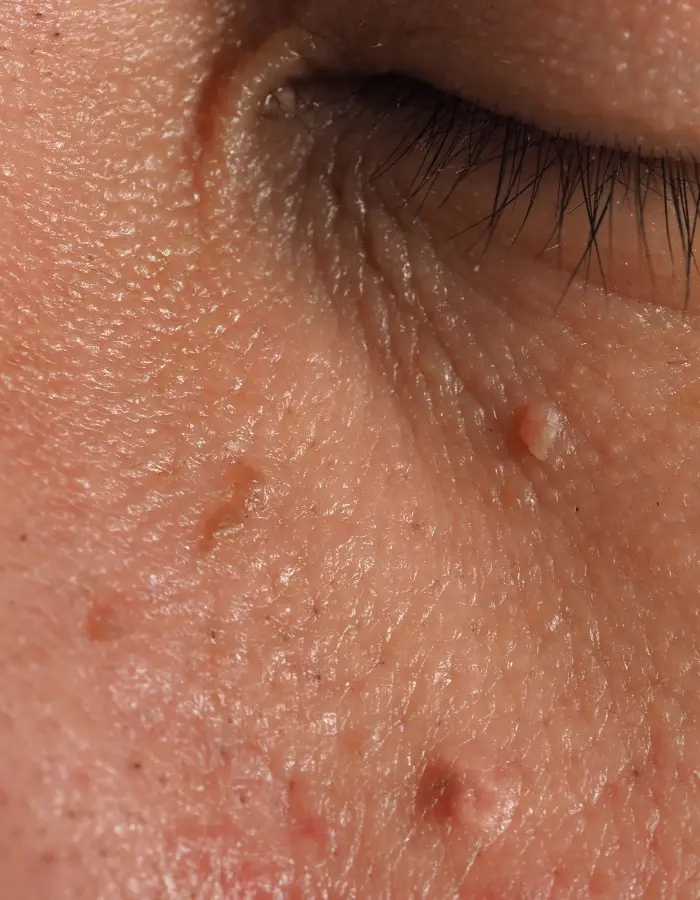
What is Warts?
Warts are small, rough growths caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). They commonly appear on hands, feet, and other parts of the body.
Warts are benign skin growths caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). They appear as small, rough bumps on the skin and can occur anywhere on the body, though they are most common on the hands, feet, and face. Warts vary in appearance, ranging from flat and smooth to raised and rough, and they can be skin-colored, pink, or darker.
While warts are generally harmless, they can be bothersome, painful, or cosmetically displeasing. They are contagious and can spread through direct contact with a wart or indirectly through surfaces touched by someone with warts. Treatment options include topical medications, cryotherapy, laser treatment, and surgical removal. Proper hygiene and avoiding direct contact with warts can help prevent their spread.
Immense Care
We aim to provide immense care tailored to manage and treat your health condition. Be assured, you are in safe hands!
Modern Techniques
We provide modern treatments to ensure you get the quickest and most effective solution to your health conditions!
Symptoms of Warts
What are the Symptoms of Warts?
Warts are typically small, rough, and raised growths on the skin, often appearing on the hands, feet, and face. They can vary in size from a few millimeters to over a centimeter and may be flesh-colored, pink, or darker. Common warts have a rough surface with a distinct border, while plantar warts, found on the soles of the feet, can be flat and painful, resembling calluses.
Filiform warts, which are long and narrow, commonly develop on the face and neck, while flat warts are smooth and slightly raised, often appearing in clusters on the face, hands, or legs. Periungual warts grow around the fingernails and toenails, causing discomfort and sometimes interfering with nail growth.
Warts can cause discomfort or pain, especially if they are located in areas subject to pressure or friction, such as the soles of the feet or around the nails. They may also bleed if injured or picked at. Warts can spread to other parts of the body or to other people through direct contact or shared surfaces, making it important to avoid touching or scratching them.
Common Warts
These warts have a rough, raised surface and typically appear on the hands or fingers. They are usually small, round, and skin-colored or slightly darker.
Plantar Warts
Found on the soles of the feet, plantar warts are flat and can be painful when walking. They often have a rough surface and are surrounded by hardened skin.
Filiform Warts
These are long, narrow warts that often appear on the face or neck. They are flesh-colored and can grow quickly, forming finger-like projections.
Flat Warts
Smooth, slightly raised warts that appear in clusters, often on the face, hands, or legs. They are smaller and less rough than other types of warts.
Periungual Warts
These warts grow around the fingernails or toenails, causing pain and sometimes affecting nail growth. They are rough and can spread rapidly in this area.
Discomfort and Pain
Warts can cause discomfort or pain, especially in areas subject to pressure or friction, such as the soles of the feet, leading to difficulty walking.
Diagnosis of Warts
1
Visual Examination
A dermatologist examines the wart's appearance, including its size, shape, and location, to distinguish it from other skin lesions.
2
Dermatoscopy
A dermatoscope magnifies the wart, allowing for a detailed examination of its structure and helping to differentiate it from other similar skin growths.
3
Biopsy
A small sample of the wart tissue may be taken for laboratory analysis to rule out other skin conditions and confirm the diagnosis of a wart.
4
Patient History
Reviewing the patient's medical history, including previous warts and immune status, helps in assessing the likelihood of recurrence and planning treatment.
5
Differential Diagnosis
The dermatologist considers other conditions, such as skin tags, calluses, or cancerous growths, to ensure an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
6
Follow-Up Monitoring
Regular follow-up appointments may be necessary to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and check for any recurrence of warts.
Book Your Appointment
Find Solution to Warts Now!
Meet Our Expert Warts Specialists


Treatment of Warts
How is Warts treated?
Treatment for warts aims to remove the growths and prevent their recurrence. Over-the-counter topical treatments, such as salicylic acid, can be effective for smaller warts. These treatments work by gradually peeling away the wart tissue. Cryotherapy, a common in-office treatment, involves freezing the wart with liquid nitrogen, causing it to blister and eventually fall off.
For larger or more persistent warts, a dermatologist may recommend laser treatment, which uses focused light to destroy the wart tissue. This method is particularly useful for warts that are resistant to other treatments or located in sensitive areas. Surgical removal, including curettage and excision, is another option for stubborn warts, often used in conjunction with other treatments to ensure complete removal.
In some cases, immune therapy, which involves stimulating the body's immune response to target the wart virus, can be used for persistent warts. This may include topical treatments like imiquimod or injections. It is important to follow the dermatologist's advice for post-treatment care to prevent recurrence and spread of the virus. Regular monitoring and early treatment can help manage warts effectively.
Topical Treatments
Over-the-counter treatments containing salicylic acid can help remove warts by peeling away the infected tissue over time, requiring consistent application.
Cryotherapy
Liquid nitrogen is applied to freeze the wart, causing it to blister and fall off within a few weeks. This is a common and effective treatment for various types of warts.
Laser Treatment
A laser is used to destroy the wart tissue, especially for resistant or sensitive area warts. This method is precise and minimizes damage to surrounding skin.
Surgical Removal
Options include curettage, where the wart is scraped off, or excision, where it is cut out. These methods are often combined with other treatments to ensure complete removal.
Immune Therapy
Treatments like imiquimod or injections stimulate the immune system to attack the wart virus, particularly effective for persistent or recurring warts.
Electrosurgery
This involves burning the wart with an electrical current, effectively destroying the wart tissue. Often used for difficult-to-treat warts that have not responded to other methods.
Causes of Warts
1
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
Warts are caused by various strains of HPV, which infect the top layer of the skin, leading to rapid cell growth and the formation of warts.
2
Direct Contact
Warts can spread through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person or by touching surfaces contaminated with the virus.
3
Broken Skin
Cuts, scrapes, or other skin breaks increase susceptibility to HPV infection, facilitating the entry of the virus and wart formation.
4
Communal Areas
Walking barefoot in communal showers, locker rooms, or pool areas increases the risk of contracting HPV and developing plantar warts.
5
Weakened Immune System
Individuals with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to HPV infections and the development of warts, as their bodies are less able to fight off the virus.
6
Skin Maceration
Prolonged exposure to moisture, which softens the skin, can create an environment conducive to HPV infection and wart development.
How to Prevent Warts?
Warts are small, rough growths caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). They commonly appear on hands, feet, and other parts of the body.
Preventing warts involves minimizing direct contact with infected areas and practicing good personal hygiene. Avoid touching warts on yourself or others and do not share personal items like towels or razors. Wear protective footwear in communal showers, locker rooms, and pool areas to reduce the risk of contracting the virus.
Keep your skin clean and dry, and avoid walking barefoot in public spaces. Strengthening your immune system through a healthy diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep can also help reduce your susceptibility to warts.